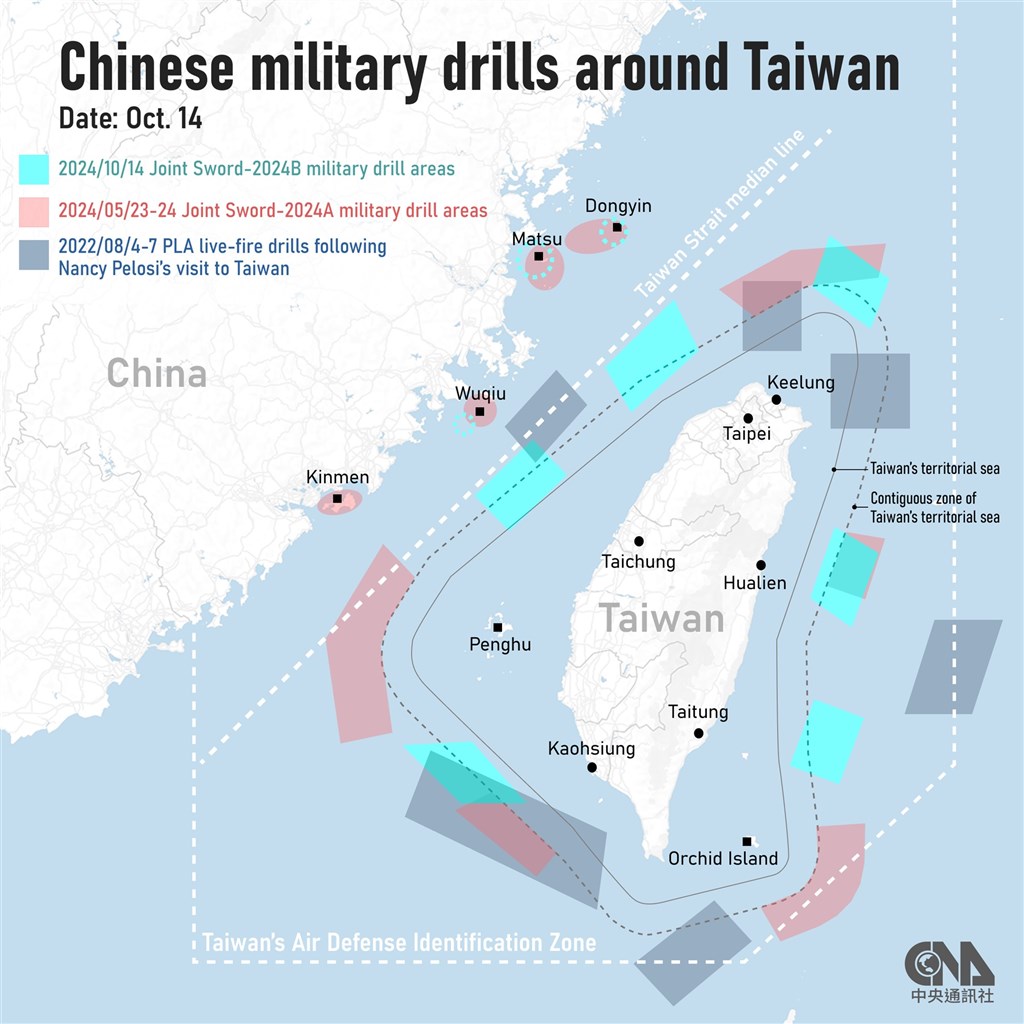
- China launched large-scale military drills around Taiwan, involving ships, aircraft, and its first aircraft carrier, as part of "Joint Sword 2024-B" exercises (BBC.com).
- The drills simulated attacks on Taiwan by land, sea, and air, testing China's joint operations capabilities and serving as a warning to pro-independence forces in Taiwan (NBCNews.com).
- Taiwan tracked a record 125 aircraft and 34 naval vessels during the exercises, including incursions into its air defense identification zone (BusinessInsider.com).
- The drills were a response to recent comments made by Taiwan's President Lai Ching-te, who rejected China's sovereignty claims over the island during Taiwan's National Day (NYTimes.com).
- U.S. officials expressed concern over the drills, warning that they could escalate tensions and destabilize the region (WashingtonPost.com).
From China's viewpoint, the military drills are a necessary demonstration of its military might and its commitment to reunify Taiwan with the mainland. China sees Taiwan as a breakaway province and views actions such as these as legitimate exercises of power to reinforce its territorial claims. Beijing frames the drills as a response to provocative statements by Taiwanese leaders and emphasizes the importance of maintaining national unity and sovereignty over Taiwan, even through military force if necessary.
Taiwan interprets these drills as acts of intimidation and aggression from China, aimed at undermining Taiwan's sovereignty and democracy. From Taiwan's perspective, the country has the right to self-governance and to resist any annexation attempts by China. Taiwan views these exercises as an attempt to destabilize the region and provoke fear among its citizens while it remains committed to defending its democratic way of life and maintaining its status as a separate entity from China.
International actors, particularly the United States, view these drills as destabilizing actions that could escalate tensions in the region and pose risks to peace and stability. The U.S. and its allies are concerned that China’s growing military presence around Taiwan is not only a threat to Taiwan’s independence but also a challenge to the broader international order. While calling for restraint, these actors emphasize the importance of maintaining open dialogue and preventing military conflict, recognizing the broader geopolitical implications of China’s actions.
Details
Security
Bias
Deltas
China recently conducted large-scale military drills around Taiwan in what has been widely described as a show of force aimed at Taiwan's leadership and its calls for independence. According to BBC.com, these exercises, known as "Joint Sword 2024-B," involved a significant mobilization of military assets, including warships, aircraft, and China’s first aircraft carrier. The drills were initiated after Taiwan’s President, William Lai, delivered a speech on Taiwan’s National Day, where he emphasized the island’s intention to "resist annexation" by China. Lai’s comments prompted a swift response from Beijing, which has consistently maintained that Taiwan is a breakaway province and vowed to reunify it with the mainland, by force if necessary. China claimed these exercises tested its ability to attack Taiwan by land, sea, and air and demonstrated its preparedness to carry out joint military operations (BBC.com).
During the drills, Taiwan reported detecting 125 Chinese aircraft and 34 naval vessels surrounding the island, which included incursions into Taiwan’s air defense identification zone (ADIZ), according to BusinessInsider.com. These numbers represented record-high levels of military activity, with 57 aircraft entering Taiwan’s ADIZ in a single day. In a notable display of military coordination, China deployed the CNS Liaoning, its first aircraft carrier, to the region, where it was involved in exercises off Taiwan’s southeastern coast. The Chinese military stated that these drills were designed to simulate a blockade of key Taiwanese ports and test joint operations capabilities between various military branches, including the army, navy, and air force. Beijing framed these actions as a necessary warning to Taiwan, reiterating its opposition to any separatist attempts by the island's government (BusinessInsider.com).
Taiwan condemned the drills, calling them "irrational and provocative" and asserting its right to self-defense. Taiwan's Ministry of National Defense confirmed that its military forces were closely monitoring Chinese movements and were prepared to respond to any escalation. The drills, described by Chinese media as a stern message to Taiwan’s pro-independence forces, were seen by Taiwan as an attempt to destabilize the region and exert pressure on the island’s democratic system. In a statement, Lai reaffirmed Taiwan’s commitment to safeguarding its sovereignty and its willingness to engage in dialogue with Beijing, though he emphasized that Taiwan would not bow to military intimidation (NYTimes.com). Taiwan has frequently been the target of Chinese military exercises, with similar large-scale drills taking place earlier in 2024, during which China simulated military assaults on Taiwan after Lai's inauguration (USAToday.com).
The international community has expressed concern over the potential for these drills to escalate tensions in the Taiwan Strait. The United States, a key ally of Taiwan, condemned the military exercises, urging China to act with restraint. According to WashingtonPost.com, U.S. officials warned that the drills could destabilize the region and that China’s military actions appeared to be a response to routine political statements made by Taiwan’s leadership. While the U.S. has long supported Taiwan’s defense against potential Chinese aggression, it has also called for peaceful dialogue between the two sides. The exercises have raised concerns not only about Taiwan’s security but also about the broader geopolitical stability in East Asia, with analysts noting that China’s growing military presence in the region is becoming increasingly normalized.
The drills are part of a broader trend in which China has ramped up its military activities near Taiwan in recent years. According to NBCNews.com, China’s frequent military exercises are seen as efforts to pressure Taiwan and exhaust its military resources. While China has previously used live ammunition in drills around Taiwan, this time it refrained from announcing no-fly zones or delineating specific activity areas. Despite the growing tensions, most observers believe that the risks of a direct military conflict between China and Taiwan remain low in the short term, largely due to the presence of U.S. forces in the region and the deterrent effect they provide (NBCNews.com). Still, the ongoing situation highlights the delicate balance of power in the Taiwan Strait and the broader implications for regional security.
The article focuses on China’s aggressive rhetoric and the scale of the military exercises, calling attention to Taiwan's warnings and the potential for increased conflict. It frames China’s actions as a forceful response to Taiwan’s leadership, thus creating a slightly negative portrayal of China.
Read full article
Negative
Sentiment
The article neutrally reports both China’s justification for the drills and the concerns expressed by the United States. It avoids taking a clear stance, presenting the information in a balanced way, mentioning both the military rationale for the exercises and international criticisms.
Read full article
The article reports on the drills while also quoting Chinese military officials and Taiwan's concerns. It presents both China’s justification for the exercises and Taiwan's condemnation, balancing the perspectives without leaning towards either side.
Read full article
The article offers a straightforward report on China’s military maneuvers and Taiwan’s response without adding any subjective commentary. Both sides are given a platform to express their positions, keeping the article neutral.
Read full article
The article presents Taiwan’s statements about defending its democracy and the nature of China’s exercises, but does not lean heavily toward criticizing or supporting either side. It presents both perspectives fairly.
Read full article
Neutral
Sentiment
The article emphasizes that the military exercises are a ‘necessary step to safeguard national sovereignty’ and repeatedly frames Taiwan as engaging in 'separatist forces.' It downplays any negative impact of the exercises, suggesting China’s actions are justified and essential for maintaining control over Taiwan.
Read full article
The article takes a clear stance by describing the exercises as a necessary 'stern warning' against separatist forces. It frames Taiwan’s independence efforts as illegitimate, while presenting China's actions as justified responses to ‘provocations’ and necessary for preserving sovereignty.
Read full article
The article highlights China’s position that the exercises are aimed at safeguarding sovereignty, portraying it as a necessary military step. It also downplays the negative consequences for Taiwan, focusing more on the legitimacy of China’s actions in the context of national security.
Read full article
The article frames China's military exercises as well-organized, necessary, and defensive in nature, focusing on the precision and strategic planning involved. Taiwan's response is downplayed, with more emphasis placed on China's objectives and military capabilities.
Read full article
Positive
Sentiment
-
+
ANNA News [Russia] Adds Strategic Justification for Military Exercises
ANNA News emphasizes China's perspective that the military drills are necessary to deter separatist forces in Taiwan.
This explanation of strategic justification for the drills is more heavily emphasized in Russian sources than in Western media. -
+
Avia.pro [Russia] Adds Tactical Details of the Drills
Avia.pro provides specifics on the tactical maneuvers of the Chinese military, including blockading key ports and simulating strikes.
This level of detail on the tactics being employed was not covered in much detail by Western articles, which tended to focus more on the geopolitical implications. -
+
Report.az [Azerbaijan] Adds Focus on Sovereignty Defense
Report.az emphasizes China's framing of the military exercises as essential for national unity and sovereignty.
This focus on the protection of sovereignty is emphasized more strongly in this article compared to Western reports. -
+
BFM.ru [Russia] Adds Precision Strike Capabilities
BFM.ru adds that the drills are focused on testing precision strikes on key targets, such as ports and military installations.
This detailed focus on precision strikes was not as prominent in Western coverage, which was more focused on the political implications. -
+
QNA [Qatar] Adds Joint Forces Involvement
QNA mentions that the drills involve coordination between land, air, and naval forces.
While this information was included in other sources, the emphasis on joint force coordination was more detailed here. -
+
Independent Arabia [Middle East] Adds Taiwan's Defensive Measures
Independent Arabia includes Taiwan’s response, detailing their defensive readiness during the Chinese drills.
This detailed look at Taiwan’s military readiness was not a focus in many of the Russian or Chinese sources.
-
-
Sky News Arabia [Middle East] Omits Taiwan’s International Support
Sky News Arabia does not mention the international support Taiwan received, which is prominent in Western articles.
The article focuses heavily on China’s military actions and threats but omits any mention of U.S. or Japanese involvement in supporting Taiwan. -
-
BFM.ru [Russia] Omits Taiwan's Criticism of China
BFM.ru does not provide much detail on Taiwan’s condemnation of China's drills, which is more prominently covered in Western media.
The article focuses on China’s military strategies but does not emphasize Taiwan’s objections or international concerns over the exercises. -
-
Avia.pro [Russia] Omits Taiwan's Defensive Position
Avia.pro omits any details about Taiwan’s defense measures, which are often covered in non-Russian sources.
The article focuses on China’s offensive military strategies but does not mention Taiwan’s readiness or their defensive stance during the exercises.